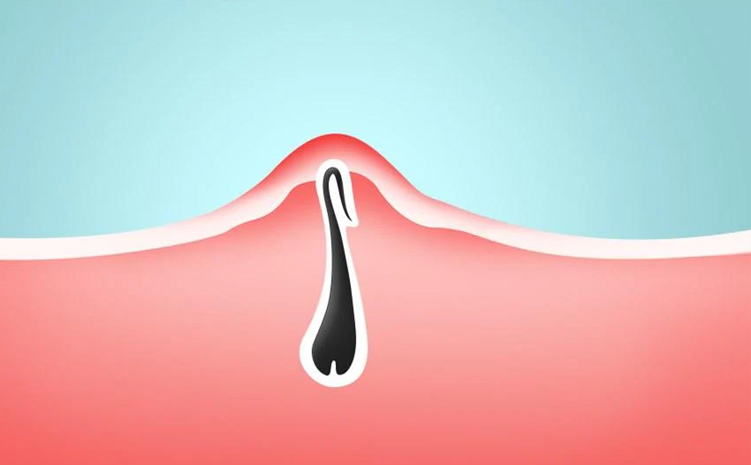
Pilonidal sinus occurs as a small opening in the intergluteal fold of the sacrococcygeal region, 3-5 cm above the anus. It is thought to develop due to hair penetrating the dermis (lower layer of the skin). Infection, chronicity and recurrence are seen with rupture into the skin. It can be seen at all ages, although it is more common in young adults (15-35). The frequency of occurrence in men is considerably higher than in women (3-4 times). For this reason, it is known as a young adult male disease.
How Does Pilonidal Sinus Occur?
The disease first manifests itself with the formation of sinus openings in the sacrococcygeal region. Hair enters the sinus openings and progresses under the skin. Hair reaching the subcutaneous tissue prepares the ground for the development of an acute abscess with the entry of bacteria. The skin is constantly trying to expel the abscess, so the disease spreads by opening new tunnels in the skin over time.
Why Does Pilonidal Sinus Form?
Although the exact cause of the disease is unknown, it is said that pilonidal sinus disease is a mechanism such as the passage of small particles such as hair and thrush accumulated in the coccyx into the subcutaneous tissue with structural forces. Since bacteria will also pass into the subcutaneous tissue along with the hair and thrush, an abscess is formed as a result of the attempt to remove the hair and thrush from under the skin, also under the influence of bacteria.
The risk factors for pilonidal sinus can be summarized as the amount of hair in the coccyx and their shedding, the coccyx being narrow and deep, not paying enough attention to the hygiene of the area, frequent sweating and diaper rash, creating an environment suitable for bacterial growth, cracks and scars in areas close to the anus, and working in jobs that require constant sitting.
What are the symptoms of pilonidal sinus?
The disease manifests itself with pain, swelling and discharge in the coccyx.
How is Pilonidal Sinus Disease Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of the disease is made by its location and appearance. The doctor who examines you can make a diagnosis by seeing the sinus openings.
What are the Degrees of Pilonidal Sinus Disease?
Pilonidal sinus is also staged as in many other diseases. The purpose of staging is to see how far the disease has progressed and to determine the treatment accordingly.
Stage 1: No discharge or abscess is observed in the patient. It is usually located on the midline. There are asymptomatic sinus openings. No procedure is performed in these patients. The patient is asked to pay attention to personal hygiene and to perform local cleaning of the area where the hair is located.
Stage 2: Patients with acute pilonidal sinus abscess. In these patients, the abscess is drained with a lateral incision. Remission is attempted with continuous dressing with antibiotics.
Stage 3: In these patients, the pilonidal sinus abscess is chronic. The patient mentions a previous abscess and discharge complaint. Chronic inflammation may be observed in the sinus opening.
Stage 4: One or more sinus openings are located on the edges of the midline. Patients state that they have experienced abscess formation and discharge complaints more than once in the past.
Type 5: Recurrence of the disease after pilonidal sinus surgery.
What are the Treatment Methods for Pilonidal Sinus?
In the presence of an abscess, drainage of the abscess is the primary treatment. In addition to drainage of the abscess, oral antibiotic treatment and frequent dressing accelerate healing. If the crystallized phenol method is to be applied, treatment can be performed in the same session following abscess drainage. If classical surgery is to be applied, the operation should be postponed to another session.
Surgical methods are used in the treatment of pilonidal sinus. Non-surgical methods are generally ineffective. Simple incision and drainage are suitable for acutely inflamed sinuses. Classical treatment is total excision and closing the wound or leaving it open. There are various methods in surgery.
These are;
Excision + leaving it to heal secondary (open technique)
Excision + primary closure
Excision + flap displacement
In the first method, the wound is not closed, it is expected to heal on its own; healing takes longer, but the risk of recurrence of the disease and the development of complications are lower. Flap displacement is a more complicated and long-lasting operation, but healing occurs quickly and the risk of recurrence of the disease is high.
How to Choose Pilonidal Sinus Treatment?
The selection of the appropriate treatment can only be made by your doctor's examination. It is best to evaluate the treatment options, advantages and disadvantages together with your doctor according to the location, prevalence and stage of the disease and to choose the most appropriate treatment.
What is Crystalline Phenol in Pilonidal Sinus Treatment?
In this method, after the anesthesia procedure, the hair in the sinus is cleaned with a clamp, and then the existing space is burned with crystallized phenol. Since no tissue excision is made, the anatomy of the area is not damaged, and intensive and painful dressings are not required during the healing process. The procedure is easy and short-lived, the risk of recurrence of the disease is quite low (0-5%), and the patient can return to his/her daily life after the surgery. It can be applied in complicated cases. For these reasons, it is a method that is frequently preferred.
What is Sinusectomy (Bascom method) in the Treatment of Pilonidal Sinus?
After local or regional anesthesia, the sinuses are reached with an incision made from the midline edge of the coccyx. After the sinus content is cleaned and scraped, each sinus opening is removed and stitched one by one. The aim of the operation is to remove only the sinus without touching the healthy tissue underneath. Recovery occurs quickly. The dressing process is easy but should not be neglected. The risk of recurrence is high compared to the phenol method. (7-16%) It cannot be applied in complicated cases.
What is the Regeneration Method in Pilonidal Sinus Treatment?
The essence of the operation is based on the removal of only diseased tissue, and healthy tissue is never interfered with. The aim here is to remove the diseased abnormal tissue that allows hair to pass into the tissue from that area, and to provide a more resistant and healthy tissue to form in its place.
Postoperative pain is very little and recovery is much faster than in classical surgeries. A simple dressing to be applied daily after the operation is sufficient. The patient can return to normal life on the first day after the operation. The recurrence rate of the disease is quite low compared to classical surgeries.
Does Pilonidal Sinus Surgery Leave Scars?
Since the surgery involves a skin incision, there will definitely be a scar. The size and shape of the scar may vary depending on the size of the incision, the amount of tissue excised, the suture style, and the patient's ability to heal. The most noticeable scar occurs after flap shift surgery, while in some methods (crystallized phenol and regeneration methods), the scar may be too small to be seen, but the treatment decision should be made not only based on this situation but also by considering all the advantages and disadvantages.
Does Pilonidal Sinus Recur?
The probability of pilonidal sinus recurrence varies between 3% and 50%. In order to prevent recurrence, you should pay attention to your personal hygiene, especially the cleanliness of the coccyx, and the prevention of sweating and diaper rash. If the hair density in the area is very high, laser hair removal can be applied.
How Can I Prevent Pilonidal Sinus?
Anatomical predisposition is important in pilonidal sinus disease. However, environmental factors are also effective in the development of the disease. Although it is not possible to completely protect against pilonidal sinus disease, the risk can be reduced with some precautions. The coccyx should be thoroughly cleaned in every bath, cotton underwear should be preferred to prevent sweating and bacterial growth, and precautions such as cleaning the area from hair at regular intervals will reduce the risk of the disease.
Regeneration
It can be applied in every case, from the simplest to the most complicated ingrown hairs. The essence of the technique can be summarized as identifying the hair entry holes and cleaning the sinus content, then excision of the hair entry holes and allowing new tissue to form. Since the newly formed tissue will be rich in fibrin, it will not allow hair to enter again. Depending on whether the disease is simple or complicated, the rest period varies between 2 hours and 1-2 days. The recurrence rate is very low. Recovery is achieved almost without leaving any scars. It is our most preferred method in suitable cases.
Microsinusectomy
This method, also known as Bascom surgery, can be performed on simple pilonidal sinuses that have not progressed. It is based on the principle of removing the sinus along with its capsule and primary closure of the remaining space. It is a method we highly prefer in suitable cases. This technique should not be used in cases with wide inter-gluteal sulcus and excessive hair. If used in such cases, unfortunately, the recurrence rate is very high. Since sutures are used, the anatomy changes slightly and if used in large, inappropriate cases, it can cause deformity. The rest period is 1-2 days. It may require partial wound care and postoperative follow-up.
Crystalline Phenol
This technique is based on the principle of expanding the hair entry holes and draining the sinus content, that is, removing the hair and infectious parts with a clamp and then cauterizing the sinus cavity with a substance called crystallized phenol. It can be applied in every case from the simplest to the most complicated hair ingrown hairs. If it is done in an appropriate manner and on the appropriate patient, the recurrence rate is very low. Recovery is achieved with little or no scarring. The rest period is 1-2 days. Complicated cases may require wound care and follow-up. It is a method we prefer very often in appropriate cases. I use this technique by modifying it. I would like to state that we have not seen any recurrence in our cases so far.
Flap Method
This technique is based on the principle of excising the sinus along with the healthy tissue around it and closing the open space by sliding the flap. It should be preferred in very complicated cases, where many sinuses are formed and the sinuses are very close to each other. In other words; it may even be the only option in such cases. It has many disadvantages. First, the operation time is long, second, recovery is achieved by leaving too many scars and creating deformities. Postoperative wound care is required. If infection develops, a very problematic recovery may occur. The resting period varies between 3-5 days. The recurrence rate is the same as microsinusectomy.